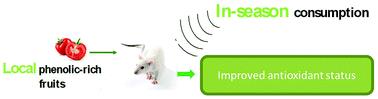
The results from our latest study entitled “Tomatoes consumed in-season prevent oxidative stress in Fischer 344 rats: impact of geographical origin”, seems to indicate this. The aim of this study was to evaluate the antioxidant properties of tomatoes consumed in-season from two different geographical origins (local LT or non-local NLT) in Fischer 344 rats.
Read moreMicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate the expression of genes associated with the development of diseases, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, the use of miRNAs to predict T2DM remission has been poorly studied. Therefore, we aimed to investigate whether circulating miRNAs could be used to predict the probability of T2DM remission in patients with coronary heart disease.
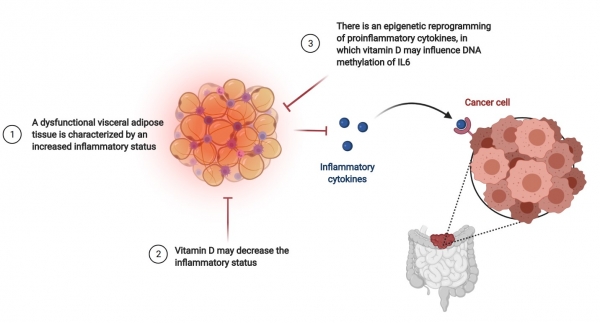
Read moreOur study suggests a possible association between epigenetic regulation of inflammatory mediators of visceral adipose tissue (VAT) in the context of colorectal cancer (CRC). This situation could be regulated, in part, by serum 25 (OH) D, as we observed an association between IL6 methylation and CRC risk, through 25 (OH) D. IL6 expression in VAT is a good prognostic factor for CRC, suggesting that IL6 could be an interesting target at HAT levels for CRC prevention.
Read more
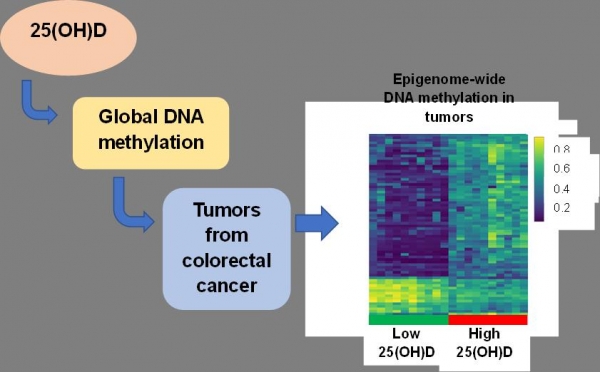
This is the first study of its kind to report a decrease in global DNA methylation in subjects with low 25 (OH) D in the context of colorectal cancer (CRC).
One of our research groups at Nutriepigen has described a new procedure that allows the selective modification of the human intestinal microbiota by using antibodies raised against surface-associated bacterial proteins specific to the microorganism of interest.
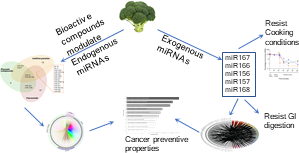
Read moreAs we know, healthy dietary habits reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases (e.g., heart disease, stroke and diabetes). A large number of studies support the preventive role of certain fruits and vegetables containing a variety of bioactive compounds in the development of these diseases. Recent findings provide evidence of how bioactive compounds (such as vitamins, lipids, miRNAs or other metabolites) present in the diet may exert their biological activity affecting consumer gene expression patterns.
Read moreIn our previous blog we mentioned bioactive compounds, and surely more than one of you have heard them somewhere.
Well, bioactive compounds are molecules that are present in foods such as fruits, vegetables and milk. They are not considered nutrients, but they have a physiological effect and therefore can have a beneficial effect on health.
These compounds can be found in the supermarket, right on the fruit shelves, and as a curious fact, these molecules are related to the color of fruits, for example the blue and red of berries.
So when you feel like eating berries for their exquisite flavor, remember that they also possess bioactive compounds such as anthocyanins, which according to the research we share today, have a beneficial effect on cardiovascular health.
Read moreYes, the sea has cucumbers! but they are not the ones we eat in our salads.
Sea cucumbers (Isostichopus badionotus) are echinoderms, like starfish and sea urchins. There are about 1,250 known species, and many of these animals are characterized by the shape of soft-bodied cucumbers.
Apart from their shape, in recent years, sea cucumbers have attracted attention for their properties in traditional medicine and as a food supplement.
APOA2 is part of the apolipoprotein superfamily that includes the apolipoprotein A1 and is the second most common apolipoprotein on the human HDL. It has been considered of minor physiological importance in lipoprotein metabolism, recent studies in rodent models have shown that APOA2 plays multiple roles in the maintenance of HDL, obesity, and blood glucose.
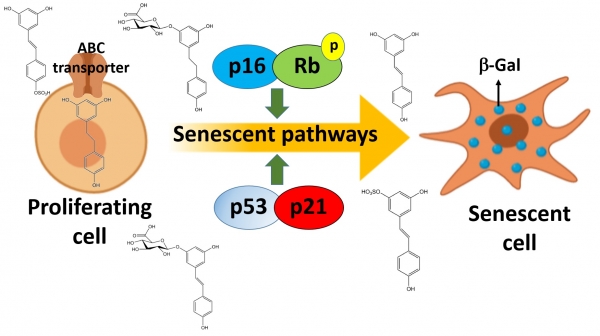
Read moreEvery year, about 1.5 million new breast cancer (BC) cases are diagnosed in women worldwide. This high incidence has aroused the interest of the scientific community, placing BC in the spotlight. The prevention or treatment of this chronic disease through diet is one of the most explored strategies hitherto. Resveratrol (RSV) is one of the most investigated phenolic compounds in the last decades.
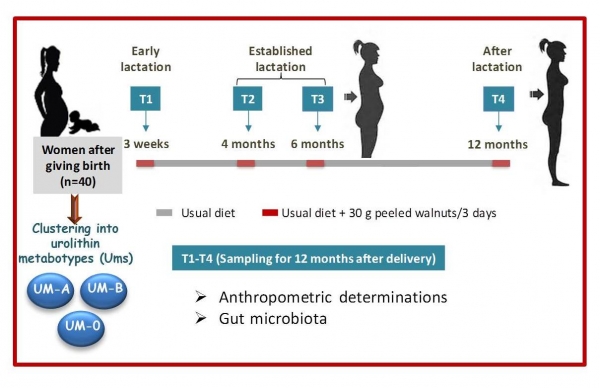
Read moreGut microbiota composition greatly varies among individuals. Some bacterial groups can metabolize dietary polyphenols, such as the ellagitannins occurring in walnuts, pomegranate, strawberries, etc., which are metabolized to the final molecules so-called urolithins (Uros). These metabolites exert in vivo anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective activity.
Read moreObesity has reached a pandemic scale worldwide, mainly caused by changes in lifestyles that include the regular consumption of high-calorie food and a critical reduction of physical activity. There is now a growing body of evidence that suggests that epigenetic mechanisms may underlie the development of metabolic disorders associated to obesity.
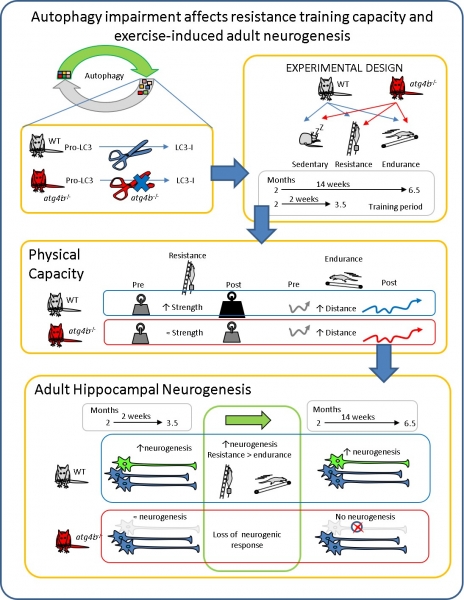
Read moreResearchers from University of Oviedo have recently published a study where the importance of autophagy, a crucial process for cellular proteaostasis maintenance which decrease with age, is analyzed within the context of resistance or endurance training adaptations.
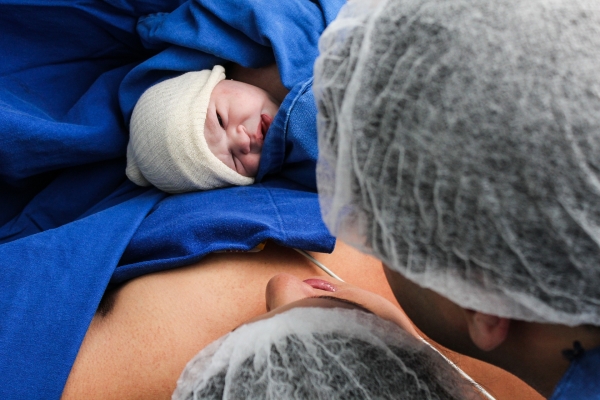
Read moreA group of researchers in the United Kingdom recently published a study in which it was found that babies born by cesarean section experience changes in their microbiome with respect to babies born vaginally.
Read moreEn un viejo número de Science Dialy tienen un buen artículo sobre genética y uno de los «personajes históricos» más curiosos de los que se pueda hablar, la Eva mitocondrial o «primigenia»: ‘Mitochondrial Eve’: Mother of all humans lived 200,000 years ago. Esta curiosa figura –a la que más o menos apropiadamente pusieron el nombre de la primera mujer del Génesis– sería, estadísticamente hablando, el ancestro común más reciente por línea materna de todos los seres humanos que hoy en día vivimos sobre la Tierra.
Read more